Customer relationship management (CRM) software has revolutionized how businesses interact with their clients. It’s no longer just about storing contact information; modern CRM systems offer powerful tools for managing sales pipelines, automating marketing campaigns, and providing exceptional customer service. This guide delves into the core functionalities, implementation strategies, and future trends of CRM software, empowering businesses to leverage its potential for growth and enhanced customer satisfaction.
From understanding the different types of CRM – operational, analytical, and collaborative – to mastering data management and security protocols, we’ll explore the critical aspects of successfully integrating and utilizing CRM within various business contexts. We’ll also examine the crucial role of CRM in customer segmentation, sales process optimization, and marketing automation, showcasing how businesses can gain valuable insights and improve efficiency across all departments.
Defining CRM Software
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is a technology for managing all your company’s relationships and interactions with customers and potential customers. The goal is simple: improve business relationships. A CRM system helps companies stay connected to customers, streamline processes, and improve profitability. It’s a powerful tool that can significantly impact a business’s success.
CRM software offers a centralized repository for all customer-related data, enabling businesses to gain a comprehensive understanding of their interactions and preferences. This consolidated view allows for more effective communication, personalized marketing, and efficient sales processes.
Core Functionalities of CRM Software
CRM systems provide a range of core functionalities designed to enhance customer interactions and business operations. These typically include contact management, sales force automation, marketing automation, customer service support, and reporting and analytics. Contact management involves storing and organizing customer information, such as contact details, purchase history, and communication logs. Sales force automation streamlines the sales process through features like lead management, opportunity tracking, and sales forecasting. Marketing automation enables targeted campaigns and personalized messaging based on customer segmentation and behavior. Customer service support facilitates efficient handling of customer inquiries and issues, often integrating with help desk systems. Finally, reporting and analytics provide valuable insights into customer behavior, sales performance, and marketing campaign effectiveness. These insights drive data-driven decision-making for improved business strategies.
Types of CRM Software
CRM systems can be categorized into three main types based on their primary focus: operational, analytical, and collaborative. Understanding these distinctions helps businesses select the most appropriate system for their needs.
Operational CRM systems directly support front-office processes like sales, marketing, and customer service. They automate tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance customer interactions. Analytical CRM systems focus on analyzing customer data to identify trends, predict future behavior, and optimize business strategies. They use data mining and business intelligence techniques to extract actionable insights. Collaborative CRM systems integrate internal and external communications, fostering collaboration among teams and enhancing customer relationships. They often incorporate features like social media integration and knowledge management systems.
Examples of CRM Software Usage Across Industries
Businesses across various sectors leverage CRM software to optimize operations and enhance customer relationships. For example, in the retail industry, CRM helps track customer preferences, personalize recommendations, and manage loyalty programs. A clothing retailer might use a CRM to send targeted email campaigns promoting new arrivals based on a customer’s past purchases. In the financial services sector, CRM systems are crucial for managing customer accounts, tracking investments, and complying with regulatory requirements. A bank might use a CRM to personalize financial advice based on a customer’s financial profile and goals. Similarly, in healthcare, CRM facilitates patient relationship management, appointment scheduling, and efficient communication. A clinic might use a CRM to track patient medical history, manage appointments, and send automated reminders. These examples illustrate the versatility and broad applicability of CRM software across different industries.
CRM Implementation and Deployment

Implementing a CRM system is a significant undertaking requiring careful planning and execution. A successful deployment translates to improved customer relationships, increased efficiency, and a better return on investment. However, challenges are common, and a strategic approach is vital to mitigate risks and ensure user adoption.
The process of CRM implementation involves several key phases, each demanding careful consideration and resource allocation. A phased approach allows for iterative improvements and minimizes disruption to ongoing business operations.
Steps Involved in CRM Implementation
Successful CRM implementation follows a structured process. While specific steps may vary depending on the organization’s size and complexity, a general framework typically includes these key stages:
- Needs Assessment and Planning: This initial phase involves defining specific business goals, identifying key performance indicators (KPIs), and understanding existing processes. A thorough analysis helps determine the appropriate CRM features and functionalities required.
- Selection and Procurement: This stage focuses on researching and selecting a suitable CRM solution, considering factors such as cost, scalability, integration capabilities, and vendor support. Negotiating contracts and establishing service level agreements are also crucial.
- Data Migration and Cleansing: Transferring existing customer data into the new CRM system requires careful planning and execution. Data cleansing is essential to ensure data accuracy and consistency, eliminating duplicates and correcting errors.
- System Customization and Configuration: This phase involves tailoring the CRM system to meet the organization’s specific needs and workflows. This may include customizing fields, creating workflows, and integrating with other systems.
- User Training and Adoption: Providing comprehensive training to users is critical for successful CRM adoption. Training should cover all aspects of the system, including data entry, reporting, and workflow management.
- Deployment and Go-Live: The actual launch of the CRM system involves careful coordination and testing to ensure a smooth transition. Post-implementation support is crucial to address any issues that may arise.
- Ongoing Monitoring and Optimization: Continuous monitoring and optimization are essential to ensure the CRM system remains effective and meets evolving business needs. Regular reviews and adjustments are necessary to maximize ROI.
Challenges During CRM Implementation
Organizations often encounter various obstacles during CRM implementation. These challenges can significantly impact the project’s success and require proactive mitigation strategies.
Effective Customer relationship management (CRM) software relies on robust infrastructure to handle large datasets and ensure accessibility. The scalability and flexibility offered by a hybrid cloud approach is increasingly important, as discussed in this insightful article on The future of hybrid cloud , which directly impacts the performance and reliability of CRM systems. Ultimately, choosing the right cloud strategy is crucial for optimizing CRM software functionality and maximizing its business value.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new systems, particularly if they are accustomed to existing workflows. Effective change management strategies are crucial to address this resistance.
- Data Migration Issues: Migrating large volumes of data can be complex and time-consuming, potentially leading to data loss or inconsistencies. Careful planning and robust data validation processes are essential.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating the CRM system with existing systems (e.g., ERP, marketing automation) can be technically challenging and require significant expertise.
- Insufficient User Training: Inadequate training can lead to low user adoption and hinder the system’s effectiveness. Comprehensive training programs are vital for successful implementation.
- Lack of Management Support: Without strong management support, CRM implementation can falter due to insufficient resources or lack of commitment.
- Cost Overruns: CRM projects can easily exceed budget if not properly planned and managed. Detailed budgeting and cost control measures are crucial.
Best Practices for Successful CRM Deployment and User Adoption
Several best practices can significantly improve the chances of a successful CRM deployment and foster user adoption. These practices focus on proactive planning, user engagement, and ongoing support.
Customer relationship management (CRM) software is crucial for business success, streamlining interactions and boosting efficiency. The rise of cloud computing has significantly impacted CRM, with many providers now offering their solutions as a service, aligning perfectly with the broader trend of Everything as a Service (XaaS). This shift allows businesses to access powerful CRM tools without significant upfront investment, ultimately improving customer engagement and driving revenue growth.
- Clearly Define Objectives and KPIs: Establish clear, measurable goals for the CRM implementation, ensuring everyone understands the expected outcomes and how success will be measured.
- Involve Key Stakeholders: Engage key stakeholders from across the organization throughout the implementation process to ensure buy-in and address concerns proactively.
- Choose the Right CRM System: Select a CRM solution that aligns with the organization’s specific needs and capabilities, considering scalability, integration, and user-friendliness.
- Provide Comprehensive Training: Offer comprehensive training programs that cover all aspects of the CRM system, including hands-on practice and ongoing support.
- Implement a Change Management Plan: Develop a comprehensive change management plan to address employee resistance and ensure a smooth transition to the new system.
- Monitor and Optimize Continuously: Regularly monitor the CRM system’s performance and make necessary adjustments to optimize its effectiveness and meet evolving business needs.
- Establish a Feedback Mechanism: Create a system for users to provide feedback on the CRM system, allowing for continuous improvement and addressing any issues promptly.
Data Management and Security in CRM
Effective Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software hinges on robust data management and unwavering security protocols. A CRM system is only as valuable as the data it holds, and the trust placed in it depends heavily on how that data is protected. This section details how CRM software manages and safeguards customer information, emphasizing the critical importance of data security and compliance.
CRM software manages customer data through a centralized database, enabling efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis. This database typically includes structured fields for various customer attributes (contact details, purchase history, interactions, etc.) and may also incorporate unstructured data like notes from customer service interactions. Sophisticated CRM systems utilize data encryption both in transit and at rest, protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access. Furthermore, access controls are implemented, limiting data visibility based on user roles and permissions, preventing unauthorized modification or deletion. Regular data backups and disaster recovery plans ensure business continuity and data preservation in the event of system failures or security breaches.
Data Security and Compliance in CRM Systems
Data security and compliance are paramount for any organization using a CRM system. Failure to adequately protect customer data can lead to severe financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Compliance with regulations like GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) and CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act) is mandatory for businesses handling personal data. These regulations dictate how data should be collected, stored, processed, and protected, requiring organizations to implement stringent security measures and provide customers with transparency and control over their data. A robust CRM security strategy incorporates various elements, including data encryption, access controls, regular security audits, employee training on data security best practices, and incident response plans. Proactive measures, such as penetration testing and vulnerability assessments, identify and address potential security weaknesses before they can be exploited.
Example Data Security Protocol for a Hypothetical CRM System
This protocol Artikels key security measures for a hypothetical CRM system named “CustomerConnect”:
- Data Encryption: All data, both at rest and in transit, will be encrypted using AES-256 encryption, a widely recognized and robust standard.
- Access Control: A role-based access control (RBAC) system will be implemented, granting users access only to the data necessary for their roles. For example, sales representatives will have access to customer contact information and purchase history, while support staff will have access to customer service interactions and case notes.
- Regular Security Audits: Internal and external security audits will be conducted at least annually to identify and address potential vulnerabilities. These audits will include penetration testing and vulnerability assessments.
- Employee Training: All employees will receive regular training on data security best practices, including password management, phishing awareness, and the importance of data confidentiality.
- Incident Response Plan: A comprehensive incident response plan will be developed and regularly tested to ensure a swift and effective response to any security incidents.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Regular data backups will be performed and stored offsite in a secure location. A robust disaster recovery plan will ensure business continuity in the event of a system failure or data loss.
- Compliance Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the system will be performed to ensure compliance with relevant data privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA.
Implementing a robust data security protocol is not a one-time effort but an ongoing process requiring constant vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats.
Reporting and Analytics in CRM
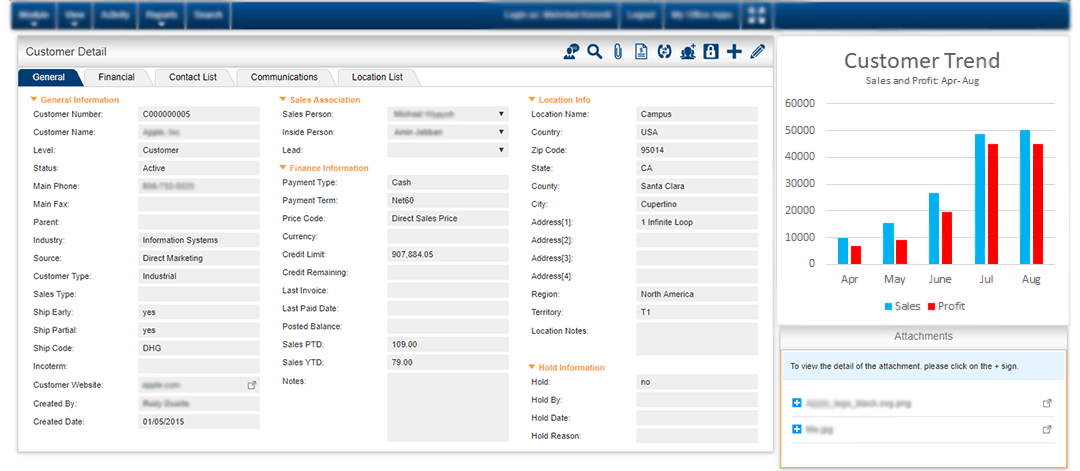
CRM systems offer powerful reporting and analytics capabilities, transforming raw customer data into actionable insights. This allows businesses to understand customer behavior, identify trends, and ultimately make better decisions to improve customer satisfaction and drive revenue growth. By leveraging the data collected within the CRM, companies can gain a comprehensive view of their customer interactions and performance across various aspects of their business.
CRM systems generate reports and analyze customer data through a combination of pre-built reports and customizable dashboards. Pre-built reports offer standard metrics and visualizations, providing a quick overview of key performance indicators. Customizable dashboards allow users to select specific data points and create tailored reports based on their individual needs and analytical goals. Sophisticated CRM systems also employ advanced analytical techniques, such as predictive modeling, to forecast future trends and behaviors. This allows businesses to proactively address potential issues and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) Tracked Using CRM Analytics, Customer relationship management (CRM) software
Understanding and tracking the right KPIs is crucial for effective CRM analytics. These metrics provide quantifiable measures of success and allow businesses to monitor progress toward their goals. A range of KPIs can be tracked, depending on the specific objectives of the organization. These often fall under categories such as sales performance, marketing effectiveness, and customer service efficiency.
Sample CRM Report for “Acme Corporation”
Acme Corporation, a fictional company specializing in software solutions, uses its CRM system to track various key metrics. The following table presents a sample report summarizing key performance indicators for Q3 2024:
| Metric | Value | Target | Variance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total Revenue | $1,500,000 | $1,400,000 | +$100,000 (7.1%) |
| Number of New Customers | 250 | 200 | +50 (25%) |
| Average Deal Size | $6,000 | $5,500 | +$500 (9.1%) |
| Customer Churn Rate | 5% | 8% | -3% |
| Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) | 4.5/5 | 4.0/5 | +0.5 |
| Marketing Campaign ROI | 150% | 120% | +30% |
| Average Resolution Time (Support Tickets) | 12 hours | 24 hours | -12 hours (50%) |
Customer Service and Support with CRM
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software significantly enhances customer service and support by centralizing customer information, streamlining communication, and automating processes. This leads to improved response times, increased customer satisfaction, and ultimately, stronger customer loyalty. A well-implemented CRM system acts as a single source of truth for all customer interactions, enabling support agents to quickly access relevant information and provide more efficient and personalized assistance.
CRM systems transform how businesses manage customer inquiries and resolve issues. By providing a structured platform for tracking and managing support tickets, CRM software eliminates the chaos of scattered emails, phone calls, and notes. This allows for better organization, improved tracking of resolution times, and more effective allocation of resources to handle customer problems. The ability to track customer interactions throughout their lifecycle allows for proactive problem-solving and the identification of recurring issues.
Managing Customer Inquiries and Resolving Issues with CRM
CRM software offers several key features that improve the management of customer inquiries and issue resolution. These features include automated routing of inquiries based on predefined rules (e.g., routing technical issues to the technical support team), centralized storage of all communication history with a customer, integrated knowledge bases for quick access to solutions, and tools for tracking the status of each inquiry, including resolution times and assigned agents. This consolidated view of customer interactions facilitates a more efficient and effective support process. For instance, if a customer contacts support via email, their query is automatically logged in the CRM, assigned to an agent, and the agent can access all previous interactions with that customer, including purchase history and previous support tickets, before responding. This contextual awareness enables a more personalized and helpful response.
Workflow for Handling Customer Support Tickets Using CRM
A typical workflow for handling customer support tickets using a CRM system might involve the following steps:
- Ticket Creation: A customer submits a support request through various channels (email, phone, web form). The CRM automatically creates a ticket, recording the customer’s information, the nature of the problem, and the contact method.
- Ticket Assignment: The CRM routes the ticket to the appropriate agent or team based on predefined rules (e.g., skill sets, availability, or the type of issue). This ensures that the ticket is handled by the most qualified individual.
- Issue Investigation and Resolution: The assigned agent investigates the issue, possibly consulting internal knowledge bases or collaborating with other team members. The agent updates the ticket with their progress and any actions taken.
- Communication and Updates: The agent communicates with the customer throughout the process, providing updates on the progress of the resolution. All communication is logged within the ticket for complete transparency and traceability.
- Ticket Closure: Once the issue is resolved, the agent closes the ticket. The CRM may automatically generate customer satisfaction surveys to gauge the effectiveness of the support provided.
- Reporting and Analysis: The CRM system provides reports and analytics on ticket resolution times, agent performance, and common issues, allowing for continuous improvement of the support process.
This structured workflow ensures that all support requests are handled efficiently and effectively, minimizing resolution times and maximizing customer satisfaction. The ability to track key metrics allows for continuous monitoring and improvement of the overall customer support process.
The Future of CRM Software: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Software
The landscape of Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software is constantly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting customer expectations. The next decade promises significant changes, impacting how businesses interact with their customers and manage their data. This section explores emerging trends and predicts the future direction of CRM.
The convergence of several technologies is reshaping the CRM experience. Artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), and big data analytics are no longer futuristic concepts; they are actively transforming CRM functionality, offering unprecedented levels of automation, personalization, and predictive capabilities. This shift is leading to more efficient processes and improved customer satisfaction.
AI-Powered CRM Enhancements
AI is rapidly becoming integral to CRM systems. AI-powered chatbots provide instant customer support, handling routine inquiries and freeing up human agents for more complex issues. Predictive analytics, fueled by ML algorithms, can anticipate customer churn, identify high-value prospects, and optimize marketing campaigns. For example, a telecommunications company might use AI to predict which customers are likely to switch providers, allowing them to proactively offer retention deals. This proactive approach improves customer loyalty and reduces churn rates significantly.
Hyper-Personalization and Customer Experience
The future of CRM hinges on hyper-personalization. By leveraging data analytics and AI, businesses can create highly customized customer journeys, tailoring interactions based on individual preferences and behavior. This means personalized product recommendations, targeted marketing messages, and proactive customer service interventions. Imagine an e-commerce platform that automatically adjusts product suggestions based on a customer’s past purchases and browsing history, providing a truly personalized shopping experience.
Integration of CRM with Other Business Systems
Seamless integration with other business systems, such as enterprise resource planning (ERP) and marketing automation platforms, is becoming increasingly crucial. A unified view of customer data across all systems allows for a more holistic understanding of customer behavior and needs. This improved data visibility enables more informed decision-making and enhances operational efficiency. For instance, sales teams can access real-time inventory data directly within their CRM, ensuring accurate order fulfillment and avoiding stock-outs.
Enhanced Data Security and Privacy
As businesses collect and store more customer data, data security and privacy become paramount. Future CRM systems will incorporate robust security measures, including advanced encryption, access controls, and compliance with evolving data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA. Transparency and customer control over their data will also be key features, fostering trust and building stronger customer relationships. This means customers will have more control over what data is collected, how it’s used, and how long it’s retained.
The Rise of Mobile-First CRM
The increasing use of mobile devices necessitates a mobile-first approach to CRM. Future CRM systems will be optimized for mobile access, providing sales teams and customer service representatives with real-time access to customer information and tools, regardless of their location. This enhances productivity and responsiveness, enabling immediate action on customer inquiries and opportunities. Field service technicians, for example, can access customer details and service history directly from their mobile devices, streamlining their workflow and improving service efficiency.
Predictive CRM and Proactive Customer Engagement
Predictive CRM will leverage advanced analytics and AI to anticipate customer needs and proactively engage them. This might involve anticipating potential problems before they arise or suggesting relevant products or services based on predicted behavior. A bank, for instance, might use predictive analytics to identify customers at risk of financial hardship and proactively offer support services, preventing potential defaults.
Ultimately, successful CRM implementation hinges on a strategic approach that aligns with specific business goals and integrates seamlessly with existing systems. By understanding the key features, navigating the challenges of deployment, and leveraging the analytical capabilities of CRM software, businesses can cultivate stronger customer relationships, optimize their operations, and achieve sustainable growth. The future of CRM is bright, with ongoing innovations promising even greater efficiency and customer-centricity.
