Workflow automation tools are revolutionizing how businesses operate, offering a powerful means to streamline processes, boost efficiency, and reduce operational costs. These tools automate repetitive tasks, freeing up employees to focus on more strategic initiatives. From simple task management to complex enterprise-wide systems, workflow automation adapts to diverse needs, impacting everything from customer service response times to project delivery schedules. The result is a more agile, responsive, and ultimately more profitable organization.
This exploration delves into the core functionalities of workflow automation tools, examining their various types, benefits, and integration capabilities. We’ll also address crucial security considerations, the process of selecting and implementing the right tool, and strategies for measuring success. Finally, we’ll look ahead at future trends and the transformative potential of emerging technologies.
Defining Workflow Automation Tools

Workflow automation tools are software applications designed to streamline and optimize business processes by automating repetitive tasks and improving collaboration. They aim to increase efficiency, reduce human error, and enhance overall productivity by managing and coordinating various steps within a workflow. This allows employees to focus on more strategic and high-value activities.
Workflow automation tools fundamentally change how businesses operate by centralizing and automating tasks, leading to significant improvements in speed, accuracy, and resource allocation.
Core Functionalities of Workflow Automation Tools
These tools typically offer a range of functionalities to support the automation process. Central to their operation are features that allow for the creation, management, and monitoring of workflows. This includes defining the sequence of steps, assigning tasks to individuals or teams, setting deadlines, and tracking progress. Further capabilities often include integration with other business applications, reporting and analytics features for performance measurement, and robust security features to protect sensitive data.
Types of Workflow Automation Tools
Several categories of workflow automation tools exist, each tailored to specific needs and scales of operation. These tools range from simple, rule-based systems suitable for small businesses to sophisticated, enterprise-grade platforms capable of managing complex, multi-departmental processes. Examples include Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tools which automate repetitive digital tasks, Business Process Management (BPM) suites offering comprehensive workflow orchestration, and low-code/no-code platforms that empower citizen developers to build and deploy automation solutions without extensive coding skills. The choice of tool depends heavily on the complexity of the workflows, the technical expertise within the organization, and the overall budget.
Common Use Cases Across Industries
Workflow automation finds applications across a broad spectrum of industries. In manufacturing, it can automate inventory management, order fulfillment, and quality control processes. In healthcare, it can streamline patient intake, appointment scheduling, and medical record management. Financial institutions utilize workflow automation for tasks such as loan processing, fraud detection, and regulatory compliance. Marketing and sales teams benefit from automation in lead nurturing, campaign management, and customer relationship management (CRM) processes. Finally, human resources departments can automate onboarding, recruitment, and performance management tasks. These are just a few examples, and the possibilities for automation are virtually limitless, constantly expanding with technological advancements.
Key Features of Workflow Automation Tools

Selecting the right workflow automation tool is crucial for streamlining operations and boosting efficiency. The market offers a wide array of options, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Understanding the key features and how they cater to different industry needs is paramount in making an informed decision. This section will delve into essential features, compare leading tools, and highlight industry-specific requirements.
A robust workflow automation tool should offer a comprehensive suite of features designed to simplify and optimize various business processes. These features often overlap, but their specific implementations and integrations vary significantly across different platforms.
Workflow automation tools have revolutionized business processes, streamlining tasks and boosting efficiency. The rise of these tools is intrinsically linked to advancements in computing infrastructure, particularly the development and widespread adoption of cloud services; understanding this connection requires examining the History of cloud computing , which paved the way for scalable and accessible platforms vital for modern workflow automation.
Ultimately, the evolution of cloud computing directly fuels the innovation and effectiveness of today’s automation tools.
Essential Features of Workflow Automation Tools
Several core functionalities are common across most effective workflow automation tools. These features form the foundation for efficient process management and should be considered when evaluating potential solutions.
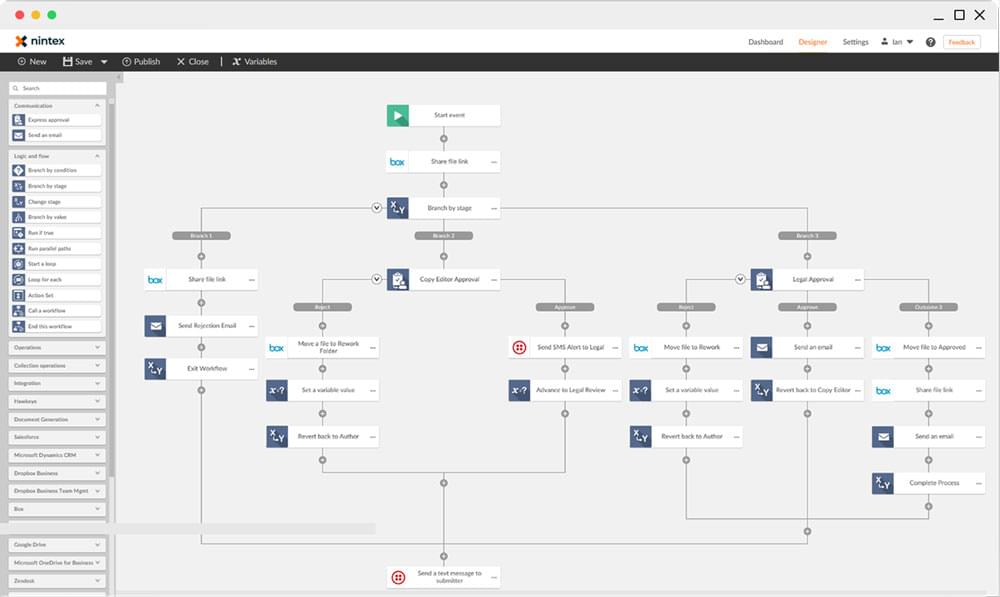
- Visual Workflow Designer: A user-friendly interface allowing users to visually map out workflows using drag-and-drop functionality, eliminating the need for complex coding.
- Integration Capabilities: Seamless integration with existing CRM, ERP, and other business applications is essential for data consistency and avoiding data silos.
- Automation Rules and Triggers: The ability to define rules and triggers that automatically initiate workflows based on predefined conditions (e.g., email received, data updated).
- Reporting and Analytics: Comprehensive reporting and analytics dashboards provide valuable insights into workflow performance, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement.
- User Management and Permissions: Robust user management features allow for granular control over access and permissions, ensuring data security and compliance.
- Scalability and Flexibility: The ability to adapt to changing business needs and scale operations as the company grows is a critical long-term consideration.
Comparison of Leading Workflow Automation Tools
Leading workflow automation tools, such as Zapier, Automate.io, Make (formerly Integromat), and Microsoft Power Automate, offer similar core functionalities but differ in their strengths and specific features. This comparison focuses on key differentiators.
| Feature | Zapier | Automate.io | Make (Integromat) | Microsoft Power Automate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | High | Medium | Medium-High | Medium |
| Integration Options | Very Wide | Wide | Very Wide | Extensive Microsoft Ecosystem Integration |
| Pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing | Subscription-based, tiered pricing, often included in Microsoft 365 plans |
| Advanced Features | Limited | Moderate | Extensive | Extensive, particularly within the Microsoft ecosystem |
Industry-Specific Workflow Automation Needs
Different industries have unique workflow requirements. The ideal workflow automation tool should be tailored to these specific needs to maximize efficiency and compliance.
Workflow automation tools significantly boost efficiency, but their cost can be a concern. Fortunately, many are now offered using a flexible Pay-as-you-go cloud pricing model, allowing businesses to scale their automation solutions according to their needs and budget. This scalability ensures that workflow automation tools remain a cost-effective investment for companies of all sizes.
- Healthcare: Tools must adhere to strict HIPAA compliance regulations, ensuring patient data privacy and security. Features like secure messaging, audit trails, and automated appointment scheduling are crucial.
- Finance: Workflow automation in finance requires robust security measures, integration with financial systems, and compliance with regulations like SOX. Automated reconciliation, fraud detection, and reporting are essential features.
- Manufacturing: Real-time tracking of inventory, automated order processing, and integration with production equipment are vital for optimizing manufacturing workflows. Tools should provide detailed production tracking and reporting.
Security Considerations for Workflow Automation Tools
Workflow automation tools, while offering significant efficiency gains, handle sensitive data throughout their operation. Robust security measures are paramount to prevent data breaches, maintain compliance, and protect the organization’s reputation. Failing to prioritize security can lead to significant financial and reputational damage.
Implementing comprehensive security measures requires a multi-faceted approach, encompassing technical safeguards, policy adherence, and ongoing monitoring. This involves careful consideration of data encryption, access control, and regular security audits to ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of processed information.
Data Encryption and Access Control
Data encryption is crucial for protecting sensitive information at rest and in transit. Workflow automation tools should employ strong encryption algorithms, such as AES-256, to safeguard data stored in databases and during transmission across networks. Furthermore, granular access control mechanisms should be implemented, limiting access to sensitive data based on the principle of least privilege. This means that users should only have access to the data and functionalities necessary for their roles. For example, a marketing team member should not have access to financial data, while a finance team member should not have access to customer health information. Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is a common and effective method for implementing this principle.
Compliance with Data Privacy Regulations
Workflow automation tools must comply with relevant data privacy regulations such as GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), CCPA (California Consumer Privacy Act), and HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act), depending on the industry and location. Compliance requires implementing appropriate technical and organizational measures to ensure the lawful processing of personal data. This includes providing individuals with control over their data, implementing data minimization principles, and maintaining accurate records of data processing activities. Failure to comply can result in substantial fines and legal repercussions.
Best Practices for Data Security
Effective data security within a workflow automation system relies on a combination of technical and procedural safeguards.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Conducting regular security audits and penetration testing helps identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses in the system before malicious actors can exploit them. This proactive approach is essential for maintaining a strong security posture.
- Secure Development Practices: Implementing secure coding practices throughout the development lifecycle of the workflow automation system is crucial. This includes using secure libraries, validating user inputs, and regularly updating the software to patch known vulnerabilities.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring users to provide multiple forms of authentication, such as a password and a one-time code generated by an authenticator app. This significantly reduces the risk of unauthorized access.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Measures: DLP tools can monitor and prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s network without authorization. This is especially important for preventing data breaches caused by accidental or malicious actions.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educating employees about security best practices and potential threats is crucial. Regular training sessions can help raise awareness and reduce the risk of human error, a major cause of security breaches.
- Incident Response Plan: A well-defined incident response plan Artikels the steps to be taken in the event of a security breach. This plan should include procedures for containing the breach, investigating its cause, and mitigating its impact.
Implementing Workflow Automation Tools
Successfully implementing workflow automation tools requires a structured approach, encompassing careful planning, execution, and ongoing monitoring. A phased implementation minimizes disruption and maximizes the return on investment. Ignoring crucial steps can lead to project delays, user resistance, and ultimately, failure to achieve desired outcomes.
The implementation process involves several key stages, each requiring dedicated attention and resources. A well-defined plan ensures that the project progresses smoothly and efficiently, leading to a successful integration of the automation tools into existing workflows.
Implementation Phases
A typical workflow automation implementation follows a phased approach. This structured methodology allows for iterative improvements and minimizes the risk of widespread errors. Each phase builds upon the previous one, ensuring a solid foundation for the entire project.
- Planning and Assessment: This initial phase involves a thorough analysis of current workflows, identifying bottlenecks and areas ripe for automation. Key stakeholders are identified and their requirements documented. The chosen automation tool is evaluated for its suitability, and a detailed project plan, including timelines and resource allocation, is created. This phase also includes defining success metrics to track progress and measure the effectiveness of the implementation.
- Design and Configuration: Based on the assessment, the workflow automation processes are designed and configured within the chosen tool. This stage involves mapping out the individual steps, defining the data flows, and setting up the necessary integrations with other systems. Thorough testing is conducted to ensure the accuracy and efficiency of the configured workflows.
- Development and Testing: This phase focuses on the actual development and testing of the automated workflows. This may involve custom coding, integration with existing applications, and rigorous testing to identify and resolve any bugs or inconsistencies. User acceptance testing (UAT) is crucial to ensure the workflows meet the needs of the end-users.
- Deployment and Rollout: Once the testing is complete, the automated workflows are deployed to the production environment. This may involve a phased rollout to minimize disruption and allow for timely adjustments based on user feedback. Comprehensive training is provided to end-users to ensure they can effectively utilize the new system.
- Monitoring and Optimization: After deployment, continuous monitoring is essential to track performance, identify potential issues, and make necessary adjustments. Regular review of the success metrics defined in the planning phase allows for ongoing optimization and improvement of the automated workflows. This phase is iterative and ensures the long-term success of the implementation.
Potential Challenges and Risk Mitigation Strategies, Workflow automation tools
Implementing workflow automation tools presents several potential challenges. Proactive risk mitigation strategies are crucial to ensure a successful implementation.
- Resistance to Change: Employees may resist adopting new tools and processes. Addressing this requires clear communication, thorough training, and demonstrating the benefits of automation. Early involvement of key stakeholders and addressing concerns proactively are essential.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating the automation tool with existing systems can be complex and time-consuming. Careful planning, selecting a tool with robust integration capabilities, and allocating sufficient time and resources for integration are vital.
- Data Migration Issues: Transferring data from existing systems to the new automation platform can present challenges. A well-defined data migration plan, including data cleansing and validation, is essential to ensure data integrity.
- Lack of Skilled Resources: Implementing and maintaining workflow automation tools requires skilled personnel. Addressing this requires investing in training or hiring individuals with the necessary expertise.
- Security Risks: Automation tools introduce new security considerations. Implementing robust security measures, including access controls, encryption, and regular security audits, is crucial to protect sensitive data.
Implementing workflow automation tools presents a significant opportunity for organizations to optimize operations and gain a competitive edge. By carefully considering the key features, integration requirements, and security implications, businesses can leverage these tools to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve employee satisfaction. The future of workflow automation is bright, with emerging technologies promising even greater levels of automation and intelligence, further streamlining processes and unlocking new possibilities for growth and innovation.
